What is a Detention Tank?

According to the American Society of Civil Engineers’ Report Card for America’s Infrastructure, municipalities are at a higher risk of stormwater runoff than ever before. More than 60% of the nation’s stormwater utilities have significant concerns about aging infrastructure handling long-term stormwater runoff control needs. Flooding is among the top three most costly and common threats to communities.
In fact, in the 2021 Report Card, it was estimated that stormwater runoff caused 9 billion dollars in damage every year.
Stormwater runoff is defined as water generated from rain or snow that flows over land or impervious surfaces (like paved roads and rooftops) and is prohibited from naturally absorbing into the ground.
Constant land development is leading to more impervious surfaces being developed which, in turn, leaves less natural soil available for stormwater to soak into. This results in higher runoff rates, increased flooding, and increases likelihood of stormwater collecting harmful pollutants along its journey to our waterways.
To combat this excess and protect our environment, many local regulators require some sort of stormwater detention system to be implemented. Stormwater infrastructure comes in many forms, but the primary one we’ll focus on in this article is a detention tank.
Let’s take a closer look into what detention tanks are, how they operate, and a few different types of systems commonly used for detention applications.
Defining Detention Tanks
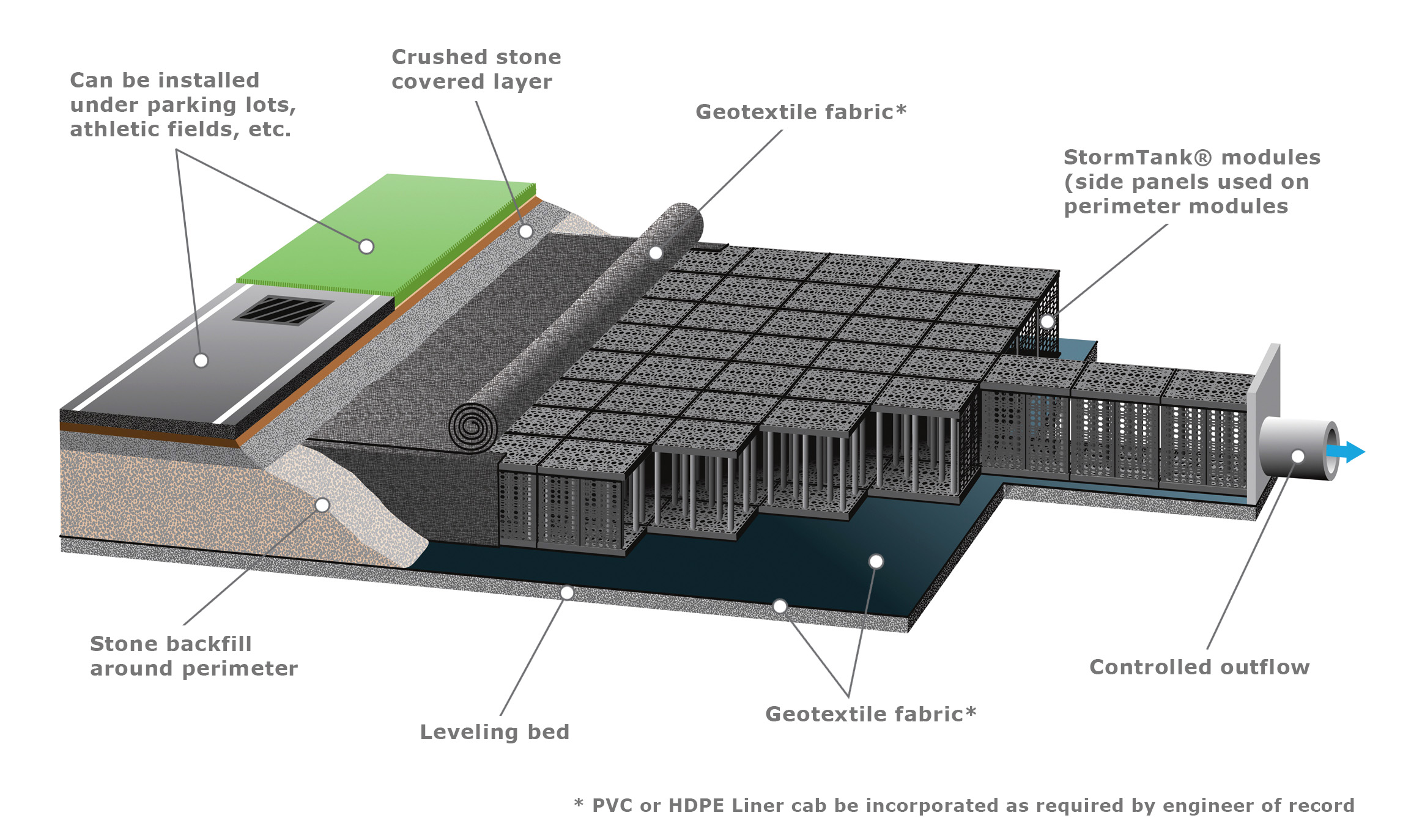 Detention tanks are artificial structures designed to temporarily hold stormwater runoff. Stormwater runoff enters these basins via storm drains. Runoff is collected until peak inflow volumes subside. From there, the detained stormwater is discharged at a controlled rate into nearby waterbodies. This method of stormwater management helps to reduce flooding in our communities and protects coastal areas from erosion.
Detention tanks are artificial structures designed to temporarily hold stormwater runoff. Stormwater runoff enters these basins via storm drains. Runoff is collected until peak inflow volumes subside. From there, the detained stormwater is discharged at a controlled rate into nearby waterbodies. This method of stormwater management helps to reduce flooding in our communities and protects coastal areas from erosion.
Best Practices for Detention Tank Design & Maintenance
To help you implement an effective detention tank system, here’s a small digestible list of best practices we’ve gathered from experience and industry standards. By following this list, you can ensure optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and functionality.
Site-Specific Design
Each site has unique characteristics that impact stormwater behavior. For example, installing your system under parking lots and athletics fields will yield different problems to overcome. Conduct a thorough site assessment to evaluate soil conditions, slope, drainage patterns, and rainfall intensity. This ensures your detention tank is correctly sized and strategically placed for maximum impact.
Ensure Proper Outflow Control
The controlled outflow must be engineered to manage peak discharge rates without overwhelming downstream infrastructure. Consider the volume of water, the elevation of your site, and the flow of water coming through your system to ensure that your outflow is properly managed.
Schedule Routine Inspections
Visual inspections should be conducted after major storms and quarterly at a minimum. While some states and municipalities might only require annual inspections, staying ahead and having a more rigorous inspection plan will help you minimize costly repairs and downtime. Look for signs of erosion, blockages, standing water, or structural damage.
Detention Tanks vs. Retention Tanks: What’s the Difference?
You may hear the terms detention tank and retention tank used interchangeably when referring to stormwater management systems, but these are two separate systems that serve different functions.
While both operate on the same general principle of managing stormwater volume to control flooding and erosion, the main difference comes from their storage methods.
Detention Tanks
Detention tanks temporarily store excess stormwater during rainfall and gradually release it back into the drainage system or nearby water bodies. These tanks help prevent downstream flooding and reduce pressure on sewer systems but do not retain water permanently. Their key features include:
● Short-term water storage
● Controlled release through an outlet
● Typically dry between storm events
Retention Tanks
In contrast, retention tanks store water permanently or for extended periods. The water may be reused on-site (for irrigation or flushing toilets) or slowly infiltrated into the ground. These systems promote water reuse and are particularly effective in areas focused on conservation. Key traits include:
● Permanent or extended storage
● Encourages infiltration or reuse
● May improve water quality through natural filtration
Common Types of Detention Tanks for Stormwater Control
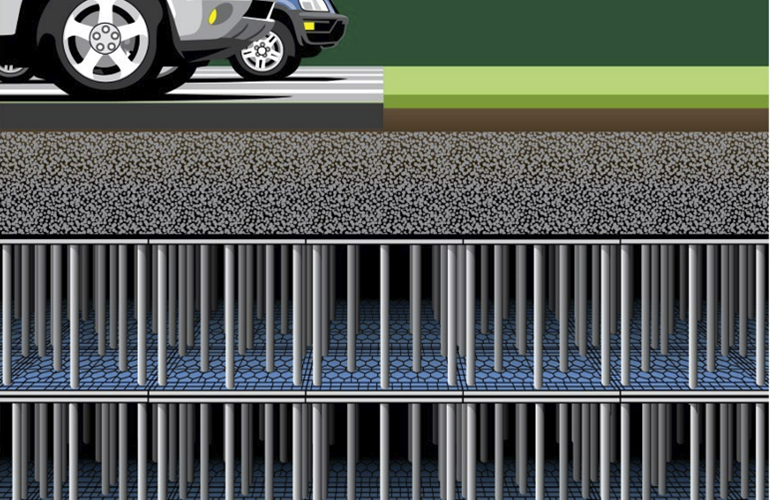
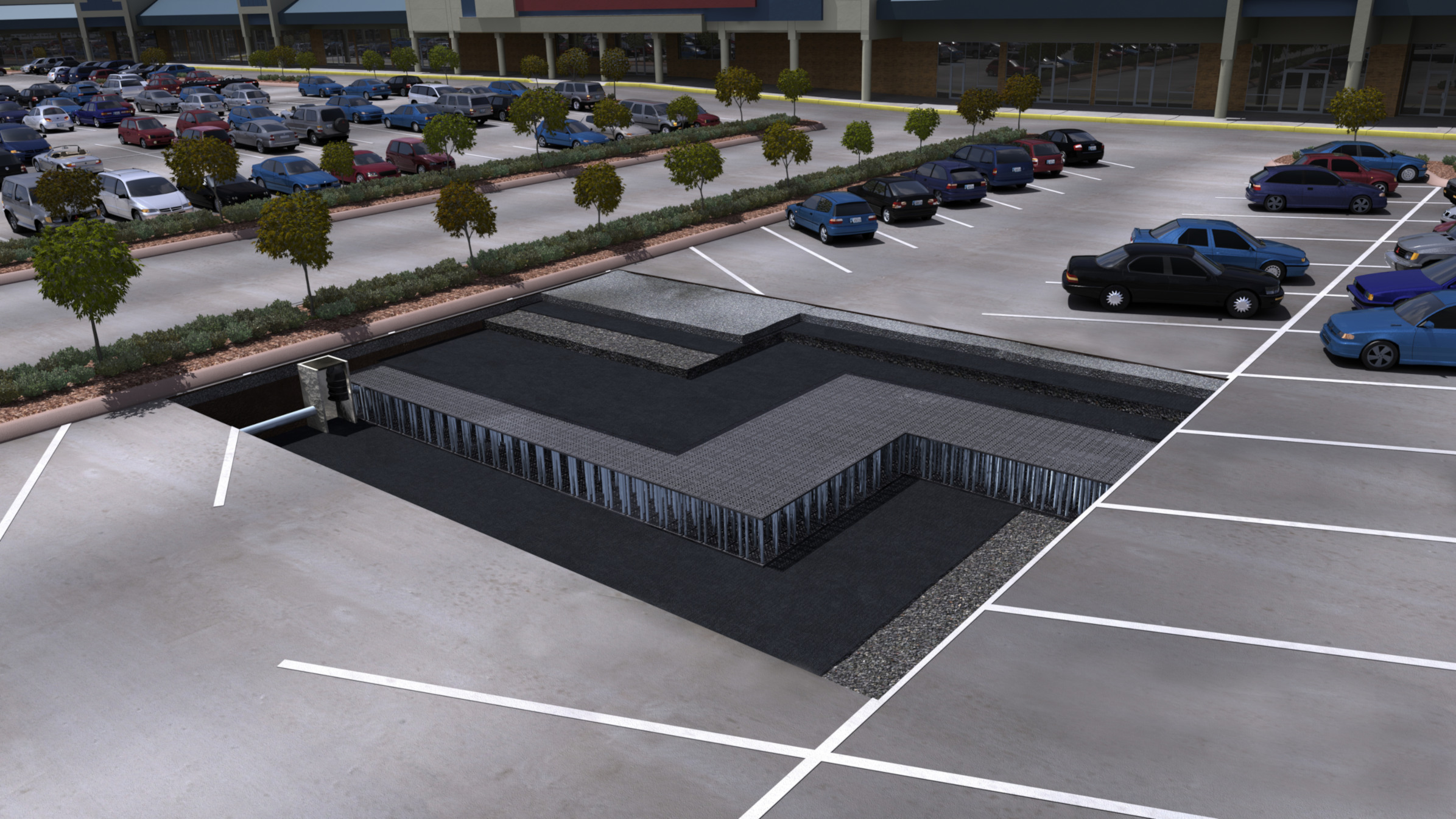 Detention systems can be installed either above ground or below ground. Traditional above ground detention systems usually entail an excavated pit that resembles a pond as it collects stormwater. While above ground systems have proven to be an effective management solution for many years, underground detention systems are better suited to maximize the amount of developable land available for construction projects. Because of this flexibility, underground detention systems are an ideal solution for applications dealing with tight spatial constraints. Most subsurface detention systems are installed beneath parking lots, lawns, athletic fields, and other hardscape surfaces.
Detention systems can be installed either above ground or below ground. Traditional above ground detention systems usually entail an excavated pit that resembles a pond as it collects stormwater. While above ground systems have proven to be an effective management solution for many years, underground detention systems are better suited to maximize the amount of developable land available for construction projects. Because of this flexibility, underground detention systems are an ideal solution for applications dealing with tight spatial constraints. Most subsurface detention systems are installed beneath parking lots, lawns, athletic fields, and other hardscape surfaces.
Brentwood offers the Module 25 series as a solution for stormwater retention, detention, infiltration, and rainwater harvesting applications.
There are two main product types currently on the market for underground detention systems: box and arch-shaped products. Both are designed to achieve the same goal of creating a void space for stormwater and supporting the surface above. However, the best type of detention system to use ultimately depends on your site-specific project. We compare both products in terms of overall footprint, capacity, buoyancy, ease of installation, and strength in our blog: Stormwater Management: Five Reasons to Use a StormTank Module Over an Arch Product.
The Bottom Line on Detention Tanks
There is no way to control the weather, and we aren’t going to have the ability for perfect grading and runoff control year-round. However, the advanced flexibility that underground detention tanks offer today provides seamless and discrete stormwater runoff control to help keep our communities as safe and clean as possible.
Detention Tank Systems with Brentwood
If you are looking for a stormwater management solution for a detention application, our industry experts are happy to discuss your site-specific needs. We have experience implementing detention tank systems across a variety of industries and applications. To see some case studies, visit our Knowledge Center. You can also use our Find A Pro search tool to locate a StormTank expert in your area who can provide professional engineering and contractor guidance for your next commercial, residential, or recreational project.